
- HOME
- 產品介紹
- 半導體事業部
- Hamamatsu Photonics
- PMT (Photomultiplier Tube)
- Photomultiplier Tube
產品介紹 Products Information
- 機器事業部
- 真空產品事業部
- 半導體事業部
- Hamamatsu Photonics
- LCOS-SLM
- UV Curing Product
- Microfocus X-Ray Source
- X-Ray Detector
- X-Ray Scintillator (CsI)
- Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS)
- X-Ray Flat Panel Sensor
- Excimer Lamp
- Lamp
- Pulsed Laser Diode
- PMT (Photomultiplier Tube)
- Avalanche Photodiode (APD)
- Optical components
- Camera
- mini-Spectrometer
- Electrostatic Removers
- MPPC (Multi-Pixel Photon Counter)
- Image Sensor
- Image Intensifiers (I.I.)
- Photodiode
- Mass spectrometry
- Flame Sensor (UVTRON®)
- Immunochromato-Reader
- Infrared Detector
- PSD (Position Sensitive Detector)
- LED
- Photo IC
- Pinhole inspection unit
- LCOS-SLM
- NJRC
- ST
- TAEJIN(HTC Korea)
- Hamamatsu Photonics
- 電子零件事業部
- 化學事業部
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 半導體IC產品
- 聯絡人: 劉小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機 619
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 電子零件產品
- 聯絡人: 林小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機618
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 真空相關產品
- 聯絡人: 王經理
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機161
聯絡資訊
Contact
- PCB機器
- 聯絡人: 王小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機631
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 化學相關產品
- 聯絡人: 陳小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機633
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 不確定品牌/型號
- 聯絡人: 陳小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機633
Photomultiplier Tube
![]() +886-2-8772-8910
+886-2-8772-8910
INTRODUCTION
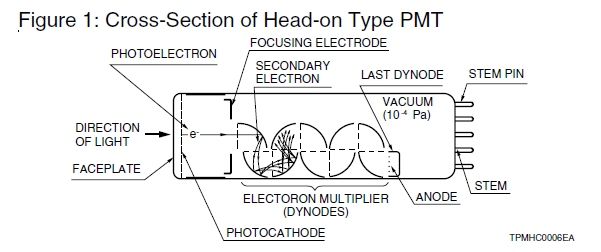
Among photosensitive devices in use today, the photomultiplier tube (or PMT) is a versatile device providing ultra-fast response and extremely high sensitivity. A typical photomultiplier tube consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) followed by focusing electrodes, an electron multiplier (dynodes) and an electron
collector (anode) in a vacuum tube, as shown in Figure 1.
When light enters the photocathode, the photocathode emits photoelectrons into the vacuum. These photoelectrons are then directed by the focusing electrode voltages towards the electron multiplier where electrons are multiplied by a secondary emission process. The multiplied electrons then are collected by the anode as an output signal.
Because of secondary-emission multiplication, photomultiplier tubes provide extremely high sensitivity and exceptionally low noise compared to other photosensitive devices currently used to detect radiant energy in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions. The photomultiplier tube also features fast time response and a choice of large photosensitive areas.
This section describes the prime features of photomultiplier tube construction and basic operating characteristics.
CONSTRUCTION
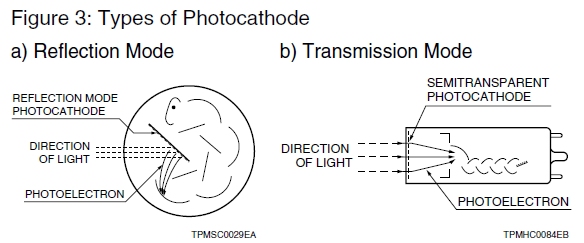
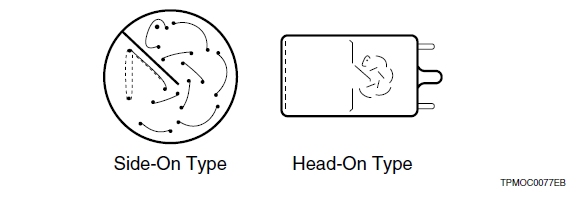
The photomultiplier tube generally has a photocathode in either a side-on or a head-on configuration. The side-on type receives incident light through the side of the glass bulb, while the headon type receives light through the end of the glass bulb. In general, the side-on type photomultiplier tube is widely used for spectrophotometers and general photometric systems. Most side-on types employ an opaque photocathode (reflection-mode photocathode) and a circular-cage structure electron multiplier (see description of "ELECTRON MULTIPLIER") which has good sensitivity and high amplification at a relatively low supply voltage.
The head-on type (or the end-on type) has a semitransparent photocathode (transmission-mode photocathode) deposited upon the inner surface of the entrance window. The head-on type provides better uniformity (see page 9) than the side-on type having a reflection-mode photocathode. Other features of head-on types include a choice of photosensitive areas ranging from tens to hundreds of square centimeters.
Variants of the head-on type having a large-diameter hemispherical window have been developed for high energy physics experiments where good angular light reception is important.

ELECTRON MULTIPLIER
The superior sensitivity (high current amplification and high S/N ratio) of photomultiplier tubes is due to the use of a low-noise electron multiplier which amplifies electrons by a cascade secondary emission process. The electron multiplier consists of 8 to 19 stages of electrodes called dynodes. There are several principal types in use today.
1) Circular-cage type
The circular cage is generally used for the side-on type of photomultiplier tube. The prime features of the circular-cage are compactness, fast response and high gain obtained at a relatively low supply voltage.
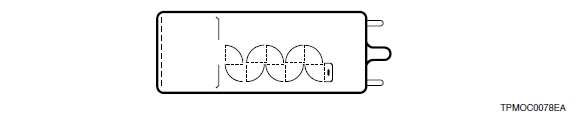
2) Box-and-grid type
This type consists of a train of quarter cylindrical dynodes and is widely used in head-on type photomultiplier tubes because of good electron collection efficiency and excellent uniformity.
3) Linear-focused type
The linear-focused type features extremely fast response time and is widely used in applications where time resolution and pulse linearity are important. This type also has the advantage of providing a large output current.
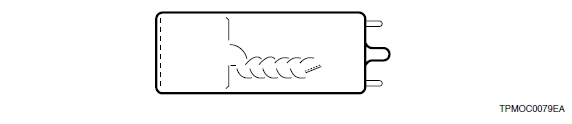
4) Box-and-line type
This structure consists of a combination of box-and-grid and linear-focus dynodes. Compared to box-and-grid type, this structure has advantages in time response, time resolution, pulse linearity, and electron collection efficiency.
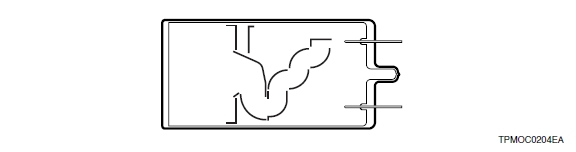
5) Circular and linear-focused type
The circular and linear-focused type has a structure that combines a circular-cage type and a linear-focused type. It offers improved pulse linearity while maintaining the compactness of the circular-cage type.
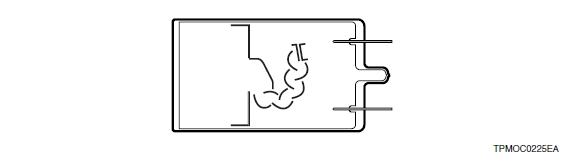
6) Venetian blind type
The venetian blind type has a large dynode area and is primarily used for tubes with large photocathode areas. It offers better uniformity and a larger output current. This structure is usually used when time response is not a prime consideration.
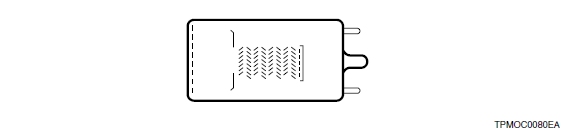
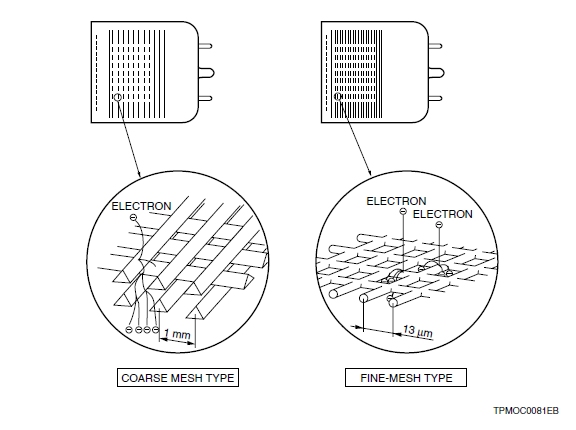
7) Mesh type
The mesh type has a structure of fine mesh electrodes stacked in close proximity. There are two mesh types of dynode: a coarse mesh type and a fine mesh type. Both types provide improved pulse linearity and high resistance to magnetic fields. The mesh type also has position-sensitive capability when used with cross-wire anodes or multiple anodes. The fine mesh type is particularly suited for use in applications where high magnetic fields are present.
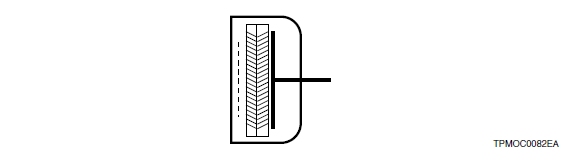
8) Microchannel plate (MCP)
The MCP is a thin disk consisting of millions of microglass tubes (channels) fused in parallel with each other. Each channel acts as an independent electron multiplier. The MCP offers much faster time response than other discrete dynodes. It also features good immunity from magnetic fields and two-dimensional detection ability when multiple anodes are used.
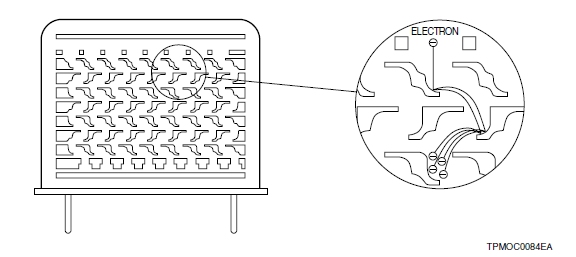
9) Metal Channel type
The metal channel dynode has a compact dynode construction manufactured by our unique fine machining techniques. It delivers high-speed response due to a space between each dynode stage that is much smaller than other types of conventional dynodes. The metal channel dynode is also ideal for position sensitive measurement.
檔案下載
Copyright © Hakuto Taiwan Ltd. All Rights Reserved.


聯絡資訊
Contact
- 半導體IC產品
- 聯絡人: 劉小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機 619
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 電子零件產品
- 聯絡人: 林小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機618
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 真空相關產品
- 聯絡人: 王經理
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機161
聯絡資訊
Contact
- PCB機器
- 聯絡人: 王小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機631
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 化學相關產品
- 聯絡人: 陳小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機633
聯絡資訊
Contact
- 不確定品牌/型號
- 聯絡人: 陳小姐
- 電話: +886-2-8772-8910 分機633